Body Fat Percentage and Its Measurement | A Comprehensive Guide
|
Body Fat Percentage Blog |
With the development of the continuously progressing era, where everybody is conscious of their body, what they are eating, and comparing themselves with the internet sensations and influencers, people worldwide have become more aware of how they look and how healthy they are. This positive perspective about a person’s health and physical presentation has changed the world’s thinking altogether. Now, people prefer a healthy and nutritious diet over gluttony. For this to happen, people tend to know their bodies’ basic structure, composition and physiology. When they know the key components of what their bodies are made of and what is required to keep them healthy, they manage their diets and physical activities accordingly.
What is Body Fat Percentage:
Body fat percentage is the fat tissue divided by your total body weight. It includes both essential body fat and storage body fat. Essential body fat is necessary for survival and is found in the heart, lungs, brain, and other organs. Storage body fat is the excess fat that accumulates in your adipose tissue (fat cells) and provides energy when needed. The average adult has a body fat percentage of 20-30%. This is the amount of fat a normal human should have, efficient metabolism, good health, and body physiology.
You might want to lower your body fat percentage for many reasons. Too much body fat can lead to health problems such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and stroke. Excess body fat can cause joint pain and interfere with physical activity. Finally, carrying excess body fat can be aesthetically unpleasing, and with the advancement of the present world, it has undoubtedly become one of the reasons to look presentable. If you want to lower your body fat percentage, you can do a few things. Read on for a comprehensive guide on reducing your body fat percentage.
Body fat percentage – An Explanation?
Body fat percentage is the total mass of fat divided by total body mass multiplied by 100. Human body fat is the adipose tissues comprising cells called adipocytes. Adipocytes are the main component of adipose tissue and are the chief storage depots of energy in the form of Triglyceride droplets. New smaller adipocytes act as powerful buffers, which avidly absorb free fatty acids and Triglycerides in the postprandial period. As it appears, the fate tissue not only makes our bodies look bulky but also has the normal function, which is essential and crucial to the efficient working of the human body.
As adipocytes grow larger, they become dysfunctional. Large adipocytes are insulin-resistant, hyper-lipolytic and resistant to the anti-lipolytic effect of insulin. (1)
Healthy Body Fat Percentage:
The distribution and amount of fat in males and females differ like any other component. According to a female’s shape and normal constitution, a healthy body fat percentage for women is 25-31%. Body fat percentage over 32% body fat for women is classified as obesity. A male body is entirely different from a female body and has a healthy body fat percentage of 18-24%. Anything over 25% is considered to be obese. This obesity caused by excess fat deposition in the body is deteriorating all the other tissues and organ systems of both male and female bodies.
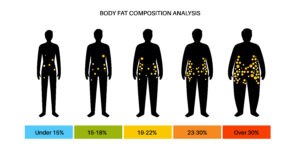
Areas of Body Fat Deposition:
In our bodies, certain nutrients and components have a certain place where they are metabolized, transported and stored. The same is the case with body fat. There are two areas of body fat storage:
- Subcutaneous Fat
- Visceral Fat
Subcutaneous and visceral fat combined store approximately 50% of dietary fat. The femora-gluteal regions, the back, and the anterior abdominal wall are the main areas for subcutaneous fat deposition. About 80% of all body fat is in the subcutaneous space. The abdominal fat is present in two main depots: subcutaneous and intra-abdominal. (1)
There is a wide range of body fat distribution in both lean and obese adults. The major environmental factors that affect body fat distribution include alcohol intake, cigarette smoking, and the timing of onset of childhood obesity. In addition, a strong genetic association seem to play a role in regional fat gain and fat loss. A predominantly upper body fat distribution, commonly associated with increased visceral fat, is associated with an abnormal metabolic profile over a wide range of body mass indexes (3).
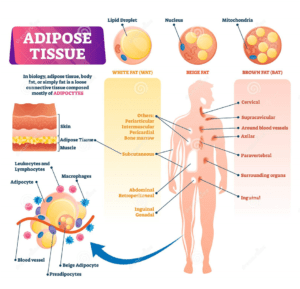
Types of Adipose Tissue:
To gain knowledge about your body fat percentage, you need to know the forms it exists in, in your body. There are two major types of adipose tissue:
White Adipose Tissue:
White Adipose Tissue generally stores excess energy in the form of triglycerides and makes up the majority of the human Body Fat percentage (BF%). Furthermore, the main functions of WAT are to protect organs against mechanical damage and release adipokines regulating various biological processes, including inflammatory reactions. (2)
Brown Adipose Tissue:
Brown Adipose Tissue, however, is mainly utilized for insulation against a cold climate. It achieves this function by generating heat as a result of dissipating energy. BAT is characterized by a high abundance of uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1), which is the protein responsible for non-shivering thermogenesis. (2)
Adipose Tissue and its Classification
Gender-based Difference in Fat Metabolism:
Under overnight postabsorptive conditions, upper body subcutaneous adipose tissue in both men and women is more lipo-lytically active than lower body adipose tissue measured by free fatty acid release per kg fat. Normal weight men and women store roughly similar proportions of dietary fat in subcutaneous and visceral fat, but this is at the cost of greater triglyceridemia in men. (3)
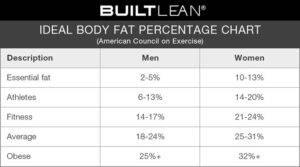
Figure 1 Ideal Body fat Percentage (10)
How to measure body fat percentage:

In the modern day and age, everyone is conscious about their health and diets to look beautiful and healthy. This positive outlook is based on the fact that they have easy access to health-related advice and guidance. When you are curious about your body fat percentage, you may wonder if there’s an accurate way to measure your body fat. Following are a few ways to measure your body fat percentage:
Circumference measurement:
Circumference measurement is another way to measure body fat at home.
This method uses a measuring tape to take measurements of specific body areas. These measurements are then put into an equation to determine body fat percentage.
Circumference measurement is considered a reliable method to measure body fat. (5)
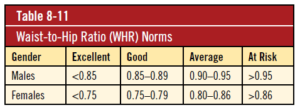 Figure 2 Wait to hip ratio chart (11)
Figure 2 Wait to hip ratio chart (11)
Skinfold calipers:
Skinfold calipers offer a cheap method to measure body fat. They’re comparatively easy to use and especially helpful for measuring body fat levels when other methods that require exclusive apparatus or specialized training are unavailable. However, you may need some assistance.
It’s usually recommended to use a 7-site measurement method when using skin calipers, which involves taking skinfold measurements from 7 sites of the body. However, 8-site and 3-site measurements can also be used (4).
|
|
Excellent |
Good |
Average |
Below average |
Poor |
|
|
Normal |
Male |
60-80 |
81-90 |
91-110 |
111-150 |
150+ |
|
Female |
70-90 |
91-100 |
101-120 |
121-150 |
150+ |
|
Body Fat Scales:

The Body fat scale evaluates the body fat and muscle mass by sending electrical currents to the body and measuring the response. Muscle and fat show different responses to electrical currents, and the scale uses these differences to determine body fat. Unlike old scales that only measure body weight, body fat scales syndicate weight scales with something called a foot-to-foot impedance meter (FFI) (6)
Waist Circumference:
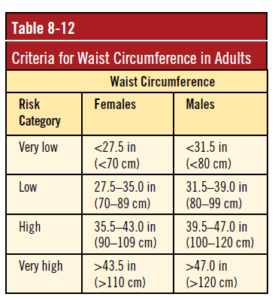
Measuring your waist circumference can give you knowledge of your body fat levels and tells if you have a high or low body fat percentage around your midsection (7)
All you need to do is place a non-stretch tape measure around your midsection above your hip bones, ensuring that the tape measure is horizontal around your waist. Keep the tape measure tight, but avoid compressing the skin.
Currently, the National Institutes of Health and the National Cholesterol Education Program have recognized waist circumference cut-off points of ≥ 40.2 inches (102 cm) for men and ≥ 34.25 inches (88 cm) for women. (8)
Figure 3 Waist Circumference Chart(12)
Methods for lowering body fat percentage:
There are many different weight loss strategies, subtypes, and commercial plans. Most include some caloric restriction and typically focus on a specific macronutrient range. (9)
Changing your dietary intake results in body composition changes. These changes can prove to be very beneficial for your body. Examples are the very low-calorie diet, which strictly limits carbohydrates and focuses on fat, the high protein diet, which limits carbohydrates and focuses on protein and a high fibre diet, which focuses on high-fibre carbohydrates. (9)
Exercise has been shown to help decrease Body Fat percentage. However, exercise is not always feasible or sustainable for everyone and does not help much unless dietary restrictions are set.
Regular exercise and dietary supplements have decreased body fat percentage to the desired value.
But the most beneficial tool that tells us How to lower the body fat percentage is lifestyle changes. A sedentary lifestyle has made man dependent on technology and machinery. Glued to our beds or chairs, continuously staring at our mobile or tablet screens, and lack of physical activity have made the human body vulnerable to the deterioration by several life-threatening factors. So, bringing a positive change and outlook will make our life less dependent on technology and more active in the physical world!
References:
(1) Ibrahim M. M. (2010). Subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue: structural and functional differences. Obesity reviews : an official journal of the International Association for the Study of Obesity, 11(1), 11–18. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-789X.2009.00623.x
(2) Atakan, M. M., Koşar, Ş. N., Güzel, Y., Tin, H. T., & Yan, X. (2021). The Role of Exercise, Diet, and Cytokines in Preventing Obesity and Improving Adipose Tissue. Nutrients, 13(5), 1459. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13051459
(3) Jensen M. D. (2008). Role of body fat distribution and the metabolic complications of obesity. The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism, 93(11 Suppl 1), S57–S63. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2008-1585
(4) Elsey, A. M., Lowe, A. K., Cornell, A. N., Whitehead, P. N., & Conners, R. T. (2021). Comparison of the Three-Site and Seven-Site Measurements in Female Collegiate Athletes Using BodyMetrix™. International Journal of exercise science, 14(4), 230–238.
- Travis M. Combest, MS, MPH, Robin S. Howard, MA, Anne M. Andrews, SP USA (Ret.), Comparison of Circumference Body Composition Measurements and Eight-Point Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis to Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry to Measure Body Fat Percentage, Military Medicine, Volume 182, Issue 7, July-August 2017, Pages e1908–e1912,
(6) Frija-Masson, J., Mullaert, J., Vidal-Petiot, E., Pons-Kerjean, N., Flamant, M., & d’Ortho, M. P. (2021). Accuracy of Smart Scales on Weight and Body Composition: Observational Study. JMIR mHealth and uHealth, 9(4), e22487. https://doi.org/10.2196/22487
(7) Ross, R., Neeland, I. J., Yamashita, S., Shai, I., Seidell, J., Magni, P., Santos, R. D., Arsenault, B., Cuevas, A., Hu, F. B., Griffin, B. A., Zambon, A., Barter, P., Fruchart, J. C., Eckel, R. H., Matsuzawa, Y., & Després, J. P. (2020). Waist circumference as a vital sign in clinical practice: a Consensus Statement from the IAS and ICCR Working Group on Visceral Obesity. Nature reviews. Endocrinology, 16(3), 177–189. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-019-0310-7
(8) Silveira, E. A., Pagotto, V., Barbosa, L. S., Oliveira, C., Pena, G., & Velasquez-Melendez, G. (2020). Accuracy of BMI and waist circumference cut-off points to predict obesity in older adults. Acurácia de pontos de corte de IMC e circunferência da cintura para a predição de obesidade em idosos. Ciencia & saude coletiva, 25(3), 1073–1082. https://doi.org/10.1590/1413-81232020253.13762018
(9) Willoughby, D., Hewlings, S., & Kalman, D. (2018). Body Composition Changes in Weight Loss: Strategies and Supplementation for Maintaining Lean Body Mass, a Brief Review. Nutrients, 10(12), 1876. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10121876
(10) Figure 1 retrieved form source: https://www.builtlean.com/ideal-body-fat-percentage-chart/
(11) Figure 2 retrieved from Source: https://www.acefitness.org/fitness-certifications/ace-answers/exam-preparation-blog/3815/anthropometric-measurements-when-to-use-this-assessment/
(12) Figure 3 retrieved from Source: https://www.acefitness.org/fitness-certifications/ace-answers/exam-preparation-blog/3815/anthropometric-measurements-when-to-use-this-assessment