Obesity | Causes and its socioeconomic effects
|
Obesity Dilemma Blog |
 Everyone is familiar with obesity, a significant health concern affecting almost 41.9% of Americans in 2017, previously 30.5% back in 2000. (1) In 2014, about 30% of the world’s population was obese. Research says that if the incidence of obesity remains at the same rate, half of the world population suffers from obesity until the end of 2030. (2)
Everyone is familiar with obesity, a significant health concern affecting almost 41.9% of Americans in 2017, previously 30.5% back in 2000. (1) In 2014, about 30% of the world’s population was obese. Research says that if the incidence of obesity remains at the same rate, half of the world population suffers from obesity until the end of 2030. (2)
According to WHO, 11% of people were obese worldwide in 2016, and its prevalence among females is more than among males. (3) Some people mix the terms obesity and overweight, but there exists a difference between these terms. Being overweight is the first step toward obesity. It is the accumulation of excessive fat leading to several health issues.
Figure 1 Shows increased waist due to abdominal obesity
Body Mass Index (BMI)
The screening test, which helps define whether a person is overweight or obese, is called Body Mass Index. It is calculated according to the following formula(4)
Interpretation of BMI
For an adult individual, the value of BMI determines whether he has an average weight or not. Everyone must check for their BMI regularly because a high BMI is health hazardous, and a low BMI has serious health consequences.
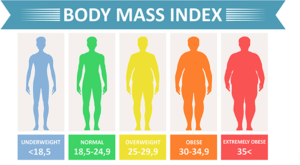
Figure 2 shows different categories of weight according to BMI
The average BMI ranges from 18.5 to 24.9 kgm-2. Below this range, it is underweighted, and above it is overweight. When someone has BMI ranging from 25 to 29.9 kgm-2, he/she stands in the category of overweight. When BMI becomes more than 30 kgm-2, then a person becomes obese. There exists a direct relation between BMI and the percentage of body fat content. A person with a high BMI is most likely to have high body fat content. Here are some interesting facts which you have to consider while understanding BMI.
- For children, BMI mainly depends upon age and sex.
- For the same BMI, females tend to have more body fat.
- For the same BMI, there exists a difference in body fat content depending on racial differences
- For the same BMI, Athletes and those who do exercise regularly have lower body fat content compared to non-athletes
The main concern here is whether a bodybuilder with having BMI higher than 25 falls under the overweight category or not. So, according to BMI, anyone having BMI greater than 25 is overweight and is at risk of suffering from the harmful consequences of a higher BMI. (5)
Causes of obesity in the modern world

When talking about the causes of obesity in the modern world, we know that the busy lifestyle is a significant reason behind it. People worldwide have less time for themselves and suffer from harmful consequences because they fail to balance their hectic daily routine and health maintenance.
As there are many reasons behind your becoming obese in addition to hectic daily life in the modern world, and these are as follows:
Figure 3 shows the hectic Lifestyle of today’s individual
High caloric intake:
The energy we get from the intake o food is measured in the form of calories. The average caloric need of an adult male is 2500 calories, and for a female, it is 2000 calories as determined by WHO. Any caloric intake greater than this value is responsible for increasing an individual’s weight; over time, it is responsible for obesity. Similarly, sedentary individuals with the recommended caloric intake and no physical activity are also at risk of developing obesity. (6)
Poor diet:
A poor diet does not mean that a person has less food to eat, but it indicates an imbalance in the consumption of different eatables. It includes excessive consumption of processed food items enriched in low-weight carbohydrates and fat, alcohol, and fizzy drinks. However, a state of depression and stressful life also serves as a risk for a person having a poor diet. (6)
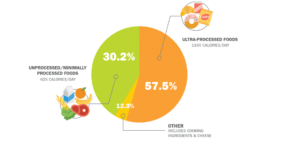
Figure 4 shows the consumption of different foods by American according to the American Institute for cancer research in 2017 (7)
In addition, it is seen that unhealthy eating habits are common in some families.
Sedentary lifestyle
 The absence of physical activity in daily life is one of the main culprits behind the development of obesity in most individuals all around the globe. People, after excessive food intake and performing their daily tasks, think that they have done enough to live a healthy life. But contrary to it, they have done nothing. So, in addition to daily activities, a proper time for physical activity in the form of any outdoor game is necessary for a healthy lifestyle. A moderate-intensity aerobic exercise for 150 minutes per week is recommended for having healthy life by the Health and Social Care Department. (6)
The absence of physical activity in daily life is one of the main culprits behind the development of obesity in most individuals all around the globe. People, after excessive food intake and performing their daily tasks, think that they have done enough to live a healthy life. But contrary to it, they have done nothing. So, in addition to daily activities, a proper time for physical activity in the form of any outdoor game is necessary for a healthy lifestyle. A moderate-intensity aerobic exercise for 150 minutes per week is recommended for having healthy life by the Health and Social Care Department. (6)
Figure 5 shows an example of a Sedentary Lifestyle
Genetical basis
In most cases, obesity is related to environmental factors. But there is a rare genetic disorder in which a person has increased appetite and is unable to lose weight. One such genetic disorder is Prader-Willi syndrome. The major gene involved in increased appetite or hyperphagia is the MC4R gene responsible for encoding melanocortin 4 receptors. (8)
Metabolic disorders
Different metabolic conditions also lead to obesity, such as.
- Hypothyroidism; a state of decreased production of thyroid hormones
- Cushing syndrome; a state of excessive steroid hormone production, mainly cortisol. (6)
Medicinal side effects
Obesity can result as a side effect of different medications such as
- Corticosteroids
- Antidepressants
- Antipsychotics
- Medication for diabetes
- Anti-epileptics
However, a smoker can also suffer from obesity after quitting smoking. (6)
Consequences of Obesity
Obesity is the 2nd major concern after smoking in the U.S., having a significant impact on societies, nations, and individuals. In the USA, obesity is also 2nd major cause of death below 70 years of age.

Obesity and Society
In societies, obese people have low self-esteem as they seek disrespect and laughter from people in their surroundings. They got lower wages as people thin obese people are unable to do adequate work at the workplace. Due to obesity, they face great discrimination in society and have a poor quality of life. Let’s take an example; no one wants to give a romantic role to an obese individual to individual. Nobody wants to marry an obese partner. Most of the time, obese individual lives a lonely life as nobody wants to be their friend. (9)
In U.S. societies, the prevalence of obesity in males is more compared to females, and people whose age ranges between 40-59 are at greater risk of suffering from obesity and its consequences. (10)
Childhood Obesity
Childhood obesity has become a major concern for modern society due to the lack of outdoor activities for our children. Research conducted over the selected countries has shown that childhood obesity rate is increasing at an alarming state.
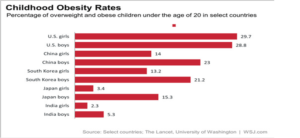
Figure 6 shows the percentages of childhood obesity in different selected countries
According to the above data, U.S. girls are the most obese, and Indian girls are the least obese. All others fall between these two extremes. (11)
Obesity and Personal Financial status
Obesity has a devastating impact on the financial status of an obese individual due to the following reasons
- Loss of job
- Lower wages
- Huge medical expenditures
- Reduced productivity at the workplace
- Retirement at an early age
- Co-morbidities
Obesity and Economy
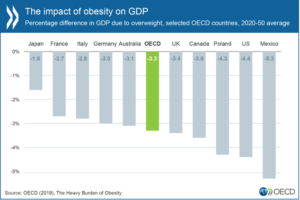
Obesity is a burden on society’s economy, and the prevalence of obesity in the community is a major concern for national stakeholders. According to a systematic literature review, obesity burdens society and the health care system. (12) The global economic impact of obesity was about 2.8% of the overall GDP of the U.S. in 2014. (2) Obesity affects economic growth of the country is due to decreased productivity at work, lost working days, disability, and mortality.
Figure 7 shows the burden of obesity on the economy of different countries of the world (13)
- The economic impact of obesity in the U.S. rose to 1.4 trillion dollars in 2020 from 976 billion dollars. (10)
- The economic cost of an adult individual ranges from 147 to 210 billion dollars per year
- Most of the economic expenditure is due to the cardiovascular and diabetic consequences of obesity.
- Obese individuals have 15 times more costs than non-obese individuals.
- Direct medical costs are related to obese males, while job-related costs such as low wages are related to obese females.
- If there is no obesity, then there will be 8.5% Medicare and 11.8% Medicaid expenditures.
Obesity and the Healthcare system
After discussing the impacts of obesity on the society and economy, we will now discuss the most critical effect of obesity and its complications, which is on the healthcare system. According to a survey, the healthcare expenditure of obese individuals is US$ 1496 more than non-obese individuals. (14)
Obesity burdens the healthcare system all around the globe, but its impact is different in different countries of the world.
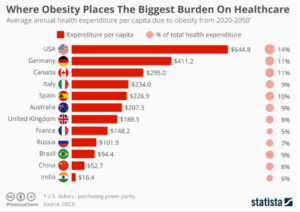
Figure 8 shows the list of countries whose healthcare systems will be most affected due to obesity from 2020 to 2050 (15)
According to the above data, the U.S. is spending most of its healthcare budget, about 14%, on the treatment of obesity which is more than any other country in the world.
Bottomline
Obesity is one of the major health issues prevailing worldwide. It not only affects the personal life of the individuals but also the economic growth of the countries. At the same time, mortality rate is increasing due to obesity and its complications, and it is burdening the healthcare system to great extent.
References:
- Ward ZJ, Bleich SN, Long MW, Gortmaker SL. Association of body mass index with health care expenditures in the United States by age and sex. PLoS ONE. 2021 Mar 1;16(3 March).
- Tremmel M, Gerdtham UG, Nilsson PM, Saha S. Economic Burden of Obesity: A Systematic Literature Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health [Internet]. 2017 Apr 19 [cited 2022 Jun 27];14(4). Available from: /pmc/articles/PMC5409636/
- Obesity and overweight [Internet]. [cited 2022 Jun 26]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight
- Bhaskaran K, Douglas I, Forbes H, dos-Santos-Silva I, Leon DA, Smeeth L. Body-mass index and risk of 22 specific cancers: a population-based cohort study of 5·24 million UK adults. The Lancet. 2014 Aug 30;384(9945):755–65.
- About Adult BMI | Healthy Weight, Nutrition, and Physical Activity | CDC [Internet]. [cited 2022 Jun 27]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/healthyweight/assessing/bmi/adult_bmi/index.html
- Obesity – Causes – NHS [Internet]. [cited 2022 Jun 27]. Available from: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/obesity/causes/
- Martínez Steele E, Popkin BM, Swinburn B, Monteiro CA. The share of ultra-processed foods and the overall nutritional quality of diets in the US: Evidence from a nationally representative cross-sectional study. Population Health Metrics. 2017 Feb 14;15(1).
- Genes and obesity | CDC [Internet]. [cited 2022 Jun 27]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/genomics/resources/diseases/obesity/obesedit.htm
- Obesity Consequences | Obesity Prevention Source | Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health [Internet]. [cited 2022 Jun 27]. Available from: https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/obesity-prevention-source/obesity-consequences/
- Economic Impact of Obesity increased to $1.4 Trillion [Internet]. [cited 2022 Jun 27]. Available from: https://milkeninstitute.org/article/economic-impact-obesity-increased-14-trillion-says-milken-institute
- China Is Now The World’s Second-Fattest Country After The U.s – Old Discussions – Andhrafriends.com [Internet]. [cited 2022 Jun 27]. Available from: http://www.andhrafriends.com/topic/515588-china-is-now-the-worlds-second-fattest-country-after-the-us/
- Tremmel M, Gerdtham UG, Nilsson PM, Saha S. Economic Burden of Obesity: A Systematic Literature Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health [Internet]. 2017 Apr 19 [cited 2022 Jun 27];14(4). Available from: /pmc/articles/PMC5409636/
- Tackling obesity would boost economic and social well-being – OECD [Internet]. [cited 2022 Jun 27]. Available from: https://www.oecd.org/newsroom/tackling-obesity-would-boost-economic-and-social-well-being.htm
- Musich S, MacLeod S, Bhattarai GR, Wang SS, Hawkins K, Frank G. Bottone Jr, et al. The Impact of Obesity on Health Care Utilization and Expenditures in a Medicare Supplement Population. Gerontology and geriatric medicine [Internet]. 2016 Jan 1 [cited 2022 Jun 27];2:233372141562200. Available from: /pmc/articles/PMC5119873/
- How much obesity costs healthcare systems around the world | World Economic Forum [Internet]. [cited 2022 Jun 27]. Available from: https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2019/10/obesity-healthcare-expenditure-burden/
- HUNT Study: Doubled Mortality Risk From Sedentary Lifestyle for 20 Years [Internet]. [cited 2022 Jun 27]. Available from: https://scitechdaily.com/hunt-study-doubled-mortality-risk-from-sedentary-lifestyle-for-20-years/